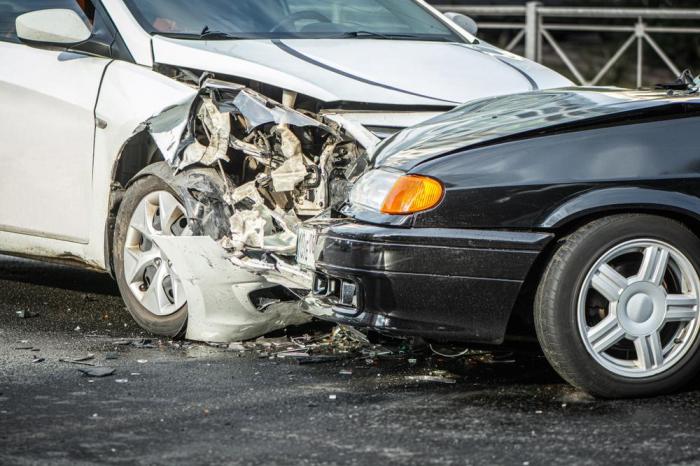
Many head on collisions occur on two lane – Many head-on collisions occur on two-lane roads, posing a significant threat to drivers and passengers. This article examines the unique characteristics of two-lane roads that contribute to head-on collisions, explores the common causes of these accidents, and discusses strategies for prevention and mitigation.
By understanding the risks and taking appropriate precautions, drivers can help reduce the number of head-on collisions on two-lane roads.
Two-lane roads are often found in rural areas and are characterized by a single lane of traffic in each direction, with no physical barrier separating opposing lanes. This design makes head-on collisions more likely to occur, as vehicles traveling in opposite directions are in close proximity and there is limited space to maneuver in the event of an emergency.
Two-Lane Roads and Head-On Collisions

Two-lane roads, with one lane for traffic in each direction, pose unique challenges that contribute to the prevalence of head-on collisions. These roads often lack physical barriers, such as medians or guardrails, to separate opposing traffic. Additionally, they typically have narrow lanes, limited sight distances, and frequent intersections, which increase the likelihood of vehicles encroaching into oncoming lanes.
Statistics indicate that head-on collisions on two-lane roads are particularly severe. According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), over 50% of fatal crashes on two-lane roads involve head-on collisions. These collisions are more likely to result in fatalities and serious injuries due to the high speeds and direct impact involved.
Factors Increasing Head-On Collision Risk
- Speeding:Excessive speed reduces reaction time and increases the severity of crashes.
- Impaired Driving:Alcohol and drug use impair judgment, coordination, and reaction time.
- Distracted Driving:Using cell phones, texting, or engaging in other distracting activities while driving can lead to inattention and lane deviations.
- Fatigue:Drowsy driving slows reaction time and impairs judgment.
- Poor Road Conditions:Narrow lanes, poor visibility, and lack of shoulders increase the risk of vehicles crossing the center line.
Causes of Head-On Collisions
Head-on collisions on two-lane roads can result from a variety of factors, including:
Driver Behavior
- Aggressive driving:Tailgating, passing in no-passing zones, and weaving in and out of traffic.
- Reckless driving:Speeding, driving under the influence, and engaging in stunts.
- Impaired judgment:Fatigue, distraction, or impaired driving can affect a driver’s ability to make sound decisions.
Road Conditions
- Narrow lanes:Narrow lanes make it difficult for vehicles to stay within their own lanes, especially when encountering oncoming traffic.
- Poor visibility:Curves, hills, and vegetation can obstruct the view of oncoming vehicles.
- Lack of shoulders:The absence of shoulders provides little room for error if a vehicle drifts out of its lane.
Vehicle Factors
- Mechanical failure:Brake or steering system malfunctions can cause vehicles to lose control and cross the center line.
- Tire blowouts:Sudden tire blowouts can cause vehicles to swerve into oncoming traffic.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies

Several strategies can be employed to prevent and mitigate head-on collisions on two-lane roads:
Road Design Improvements
- Rumble strips:Rumble strips on the edge of the road provide a tactile warning to drivers who drift out of their lane.
- Center medians:Physical barriers, such as medians, prevent vehicles from crossing into oncoming lanes.
- Improved visibility:Clearing vegetation, installing reflective markers, and improving lighting can enhance visibility for drivers.
Technology
- Lane departure warning systems:These systems alert drivers when they unintentionally cross lane lines.
- Autonomous emergency braking:These systems can automatically apply the brakes if a collision is imminent.
Public Awareness and Education, Many head on collisions occur on two lane
- Public awareness campaigns:Educating drivers about the dangers of head-on collisions and the importance of safe driving practices.
- Community outreach programs:Promoting safe driving behaviors through community events and partnerships.
- Educational materials:Distributing brochures, videos, and other materials to inform drivers about the risks of head-on collisions.
FAQ: Many Head On Collisions Occur On Two Lane
What are the most common causes of head-on collisions on two-lane roads?
The most common causes of head-on collisions on two-lane roads include driver error, such as speeding, distracted driving, and impaired driving; road conditions, such as poor visibility and slippery surfaces; and vehicle factors, such as mechanical failures and inadequate lighting.
What are some effective strategies for preventing head-on collisions on two-lane roads?
Effective strategies for preventing head-on collisions on two-lane roads include improving road design, such as adding rumble strips and center medians; implementing traffic calming measures, such as speed limits and stop signs; and promoting safe driving practices, such as avoiding distractions and never driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
What role does public awareness and education play in reducing head-on collisions on two-lane roads?
Public awareness and education campaigns can play a vital role in reducing head-on collisions on two-lane roads by informing drivers about the risks and encouraging them to adopt safe driving practices. Educational materials, such as brochures and videos, can help drivers understand the dangers of head-on collisions and the importance of taking precautions to avoid them.
