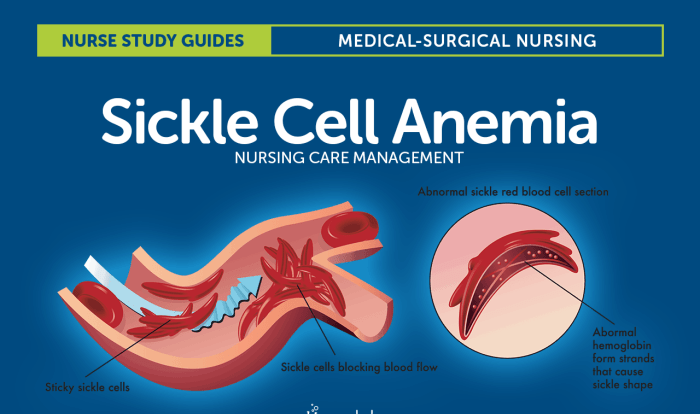
The Fluid and Electrolyte Concept Map is an essential tool for healthcare professionals to understand the complex relationship between fluids, electrolytes, and the body’s systems. It provides a comprehensive overview of fluid and electrolyte balance, imbalances, management, and assessment.
This concept map serves as a valuable resource for healthcare providers to ensure optimal patient care.
Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
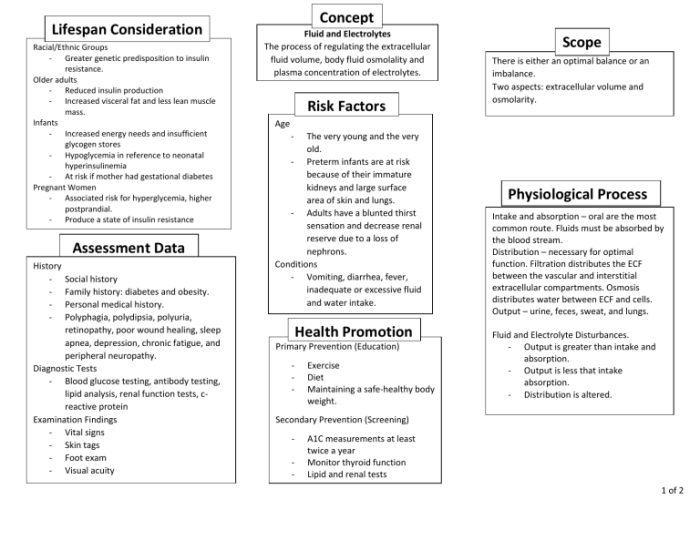
Maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance is crucial for overall health and well-being. It involves regulating the amount of water, electrolytes, and other substances in the body to ensure proper functioning of cells, tissues, and organs.
The body’s fluids are primarily composed of water, which accounts for approximately 60% of total body weight. Electrolytes are minerals that dissolve in water and carry an electrical charge, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate. These electrolytes play vital roles in various bodily functions, such as maintaining blood pressure, regulating muscle contractions, and facilitating nerve impulses.
The balance of fluids and electrolytes is maintained through a complex interplay of mechanisms involving the kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine system. The kidneys regulate the excretion of water and electrolytes through urine, while the lungs help regulate fluid balance through evaporation.
The gastrointestinal tract absorbs fluids and electrolytes from food and drink, and the endocrine system releases hormones that influence fluid and electrolyte levels.
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
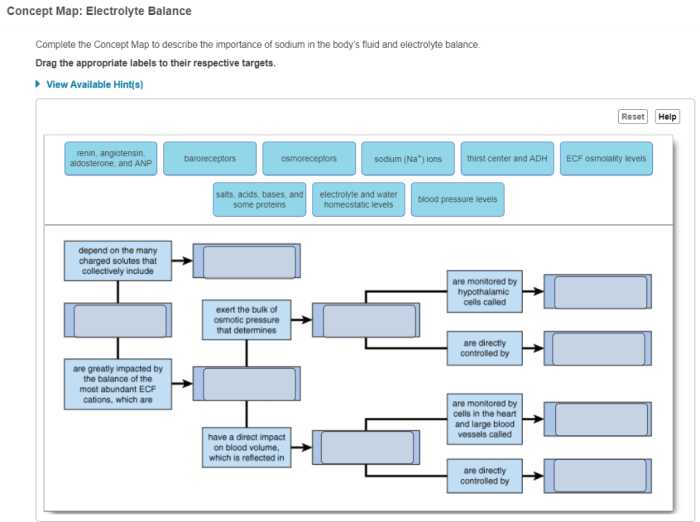
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances can occur when the body’s normal balance is disrupted. These imbalances can be caused by various factors, including excessive fluid loss (dehydration), excessive fluid intake (overhydration), or electrolyte disturbances.
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in, resulting in a decrease in total body water. This can be caused by excessive sweating, diarrhea, vomiting, or inadequate fluid intake. Overhydration, on the other hand, occurs when the body retains too much fluid, leading to an increase in total body water.
This can be caused by excessive fluid intake, impaired kidney function, or certain medical conditions.
Electrolyte disturbances can occur independently or in conjunction with fluid imbalances. These disturbances can be caused by excessive loss of electrolytes (e.g., through diarrhea, vomiting, or excessive sweating), inadequate intake of electrolytes, or abnormal electrolyte metabolism. Electrolyte imbalances can disrupt various bodily functions, including muscle function, nerve transmission, and cardiac rhythm.
Fluid and Electrolyte Management: Fluid And Electrolyte Concept Map
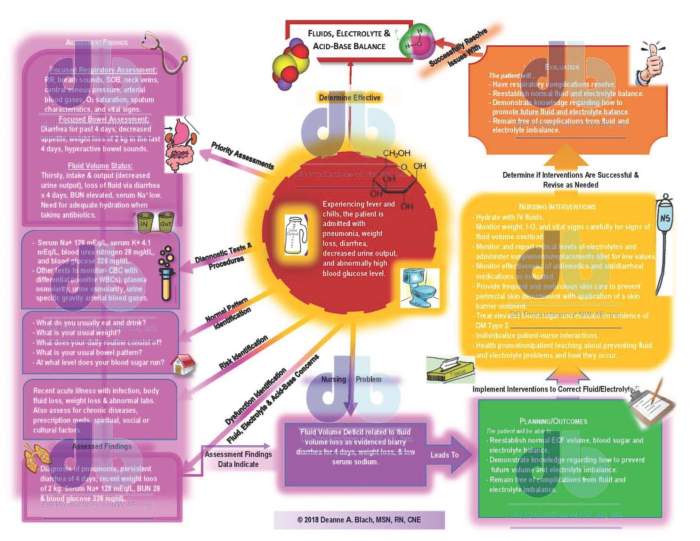
Assessing fluid and electrolyte status is essential for managing imbalances and maintaining overall health. This involves evaluating the patient’s history, physical examination, and laboratory tests.
Laboratory tests, such as blood tests and urine analysis, can provide valuable information about fluid and electrolyte levels. Blood tests can measure serum electrolyte concentrations, while urine analysis can assess urine specific gravity and electrolyte levels, which can help determine the cause of fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
Administering fluids and electrolytes can be done orally, intravenously, or through other routes depending on the severity of the imbalance. Oral fluids and electrolytes are typically used for mild imbalances, while intravenous fluids and electrolytes are used for more severe imbalances or when oral administration is not possible.
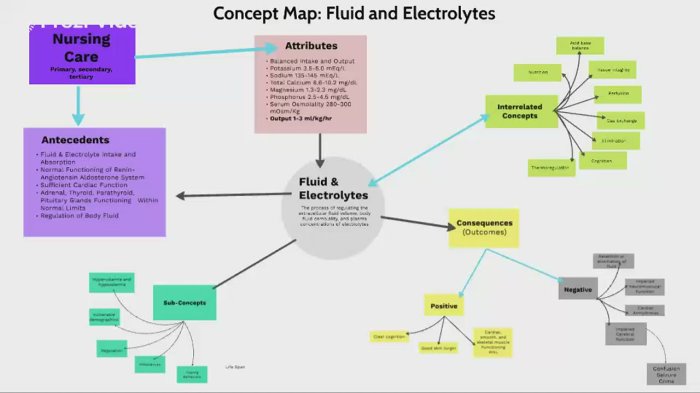
Fluid and Electrolyte Concept Map
| Fluids | Electrolytes | Body Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Water | Sodium | Cardiovascular system |
| Blood | Potassium | Nervous system |
| Interstitial fluid | Chloride | Musculoskeletal system |
| Intracellular fluid | Bicarbonate | Renal system |
The concept map above illustrates the relationships between fluids, electrolytes, and the body’s systems. It highlights the importance of maintaining a balance of these substances for optimal health.
Expert Answers
What is the importance of fluid and electrolyte balance?
Maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance is crucial for proper cell function, organ function, and overall health.
What are the signs and symptoms of fluid and electrolyte imbalances?
Signs and symptoms may include dehydration, edema, fatigue, muscle cramps, and changes in blood pressure.
How are fluid and electrolyte imbalances treated?
Treatment typically involves administering fluids and electrolytes intravenously or orally to restore balance.